Cloud computing has grown massively in the last decade, with roughly 60% of all corporate data worldwide now being stored in the Cloud. From sharing Google Docs with colleagues to watching Netflix in an evening, most of us harness the Cloud every day, even if we don’t realise it.
This trend isn’t going away either. Forecasts show the Cloud industry is going to double from 2021 to 2026, and adoption of Cloud technology has only been accelerated by the pandemic.
Cloud computing is the delivery of IT services using a network of connected computers that can process information, perform operations, and store data.
The Cloud reduces expenditure by eliminating the initial cost required to build data centres. In addition, maintenance costs from constantly powering and staffing data centres are reduced. By allowing a massive company like Amazon to handle the infrastructure costs, users benefit from economies of scale. This is because Amazon has been building servers in bulk for over 15 years, making it far cheaper for users to rent computing power from Amazon, instead of building their own data centres.
The on-demand nature of the Cloud alleviates the need to allocate redundant servers, allowing for computing power to be accessed with the click of a button when needed.
By only using and paying for computing power when needed, the Cloud elastically offers the right amount of processing. This means the Cloud can function for any business, no matter the size.
The Cloud eliminates the need for data centres to be set up, freeing up the time of internal IT staff and decision makers.
Continuity is ensured by storing data in externally accessible data centres. This makes data backup and disaster recovery much easier so your business can stay online all the time.
Cloud providers offer security features to keep their networks safe, protecting data and applications. As the biggest cloud providers are internet giants like Amazon, relying on their cloud infrastructure security is easier and safer for most businesses than trying to navigate the world of security on their own.
Cloud services like Google Docs allow team members to collaboratively share and edit documents. Files can be accessed in a shared location, so multiple colleagues can make edits from anywhere.
So how does the Cloud work?
In order to benefit from the Cloud, organisations must decide which deployment model best suits their needs. There are 4 major Cloud deployment models, these are based on the management and ownership of the hardware which drives the Cloud.
Now we’ve outlined the infrastructure behind the Cloud, let’s discuss the services which are provided.
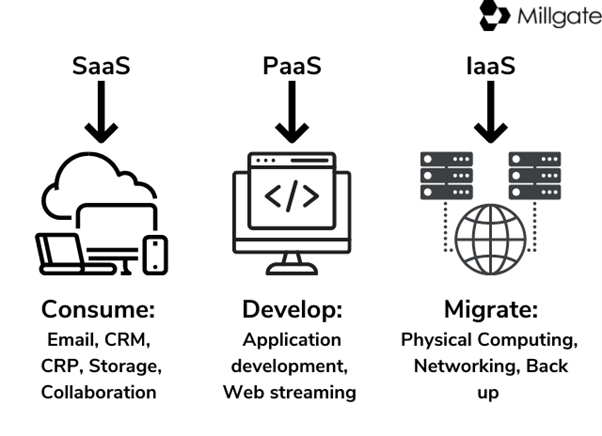
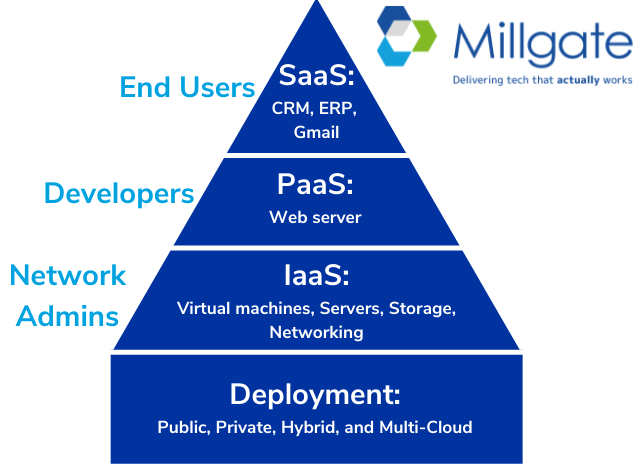
Organisations may use more than one of the following services; large businesses most likely utilise all three.
IaaS, or Infrastructure-as-a-service, provides hard drives, servers storage, virtualisation and networking, which are all managed by the Cloud provider. The customer manages everything besides the hardware, including operating systems and middleware.
PaaS, or Platform-as-a-service, provides an environment for software developers to create, deliver, test, and manage applications in the Cloud, without setting up the hardware.
SaaS, or Software-as-a-service, allows for the delivery of software applications over the internet (such as Microsoft 365). SaaS providers manage the hardware, maintenance, updates, data storage and networking associated with the Cloud. This is the most common type of service and is often delivered on internet browsers, so no installation is required.
The two largest cloud providers by market share are Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure. Both providers offer IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
AWS (Amazon Web Services) is the largest and most established Cloud provider with a 31% share of the market. Amazons 7-year head start over its competitors has also allowed AWS to provide more features than the other Cloud providers. AWS also has fewer outages; however, the variety of options can make pricing confusing.
Azure, Microsoft’s Cloud solution, offers powerful processing speed and easy integration with Microsoft software, making it a good choice for business infrastructure solutions. Azure also offers the best option for hybrid Cloud, allowing for greater customisation. However, the support and documentation for Azure is sometimes lacking, meaning considerable expertise can be required to manage and implement it effectively.
There’s an awful lot to think about with Cloud computing, especially when you look at the effects on your business. That’s why we always recommend speaking with a specialist to determine which solutions are best to utilise as part of your infrastructure.
The Cloud service you choose depends on your businesses size and goals. If you want maximum customisation, then an IaaS solution run on a hybrid cloud would provide the most options. Another use case for IaaS includes organisations lacking the capital to build their own IT infrastructure with the necessary redundancy to deal with usage spikes. However, in-house expertise is required to properly configure IaaS.
If you’re a small business or individual user and a SaaS solution offers the required functionality, then it would be the easiest option, offering the lowest costs and speediest set-up. This would be a cost-effective solution for an SMB trying to develop an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system.
Finally, if you want to write code and build applications with a team of software developers, then a PaaS solution would work best. PaaS is also a good fit for those looking to build applications and store data for IoT devices.
Regardless of which solution works best for you, the Cloud will increasingly hover over us in our everyday lives, including in our businesses, growing with the continued trend in remote working and ever improving technology.
If you still have questions, you can speak with our Solutions team at no cost or obligation to find the best way to leverage the Cloud in your business.